This article helps you understand what Proof of Stake is and how the PoS mechanism works on the blockchain, along with other useful information. Learn more here.

What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a blockchain consensus mechanism. PoS allows users to earn rewards for validating blocks on the blockchain.
In simple terms, users deposit a certain amount of assets to become validators on the blockchain.
Unlike Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin), users do not need expensive mining hardware or large amounts of electricity. Instead, the network selects individuals to validate blocks based on the amount of coins they own. The more coins owned, the higher the chance a user has of being selected to validate.
These validators verify transactions on the network and submit proofs to the block. If correct, validators are rewarded with the blockchain’s inflation or collected transaction fees. If incorrect, they are penalized by losing all or a portion of their staked assets.
What are the Characteristics of Proof of Stake?
Advantages of PoS
- No need for high-performance machines: Anyone can set up specialized nodes on their own computers or servers.
- Delegation is possible: Users can delegate their coins to validators, giving them more voting power. In return, the delegators receive a portion of the rewards without having to do any work.
- Increased scalability and transaction speed: Improves decentralization as validation can be performed by anyone staking tokens in the network, creating a more decentralized network.
- More environmentally friendly: Proof of Stake does not require the high energy consumption that Proof of Work does (like Bitcoin, for example).
Disadvantages of PoS
- Locked capital and potential for loss: When delegating or acting as a validator, users gain more coins but their capital is locked up. There’s also the risk of coin depreciation, where the rewards might not be enough to offset potential losses.
- Unlocking periods: There may be cases where unlocking staked tokens requires waiting for a certain period, which could be a week, two weeks, or more. This can leave users vulnerable to sudden price adjustments.
- Token lockup is related to governance: Those who stake more tokens have more weight in governance decisions. This is why validators also need users to delegate tokens to them. This can lead to blockchain centralization, where a small number of people have excessive power, and the project has to follow their lead, even if their opinions don’t benefit the project.
- Weaker security: Since anyone can become a validator simply by owning a large amount of tokens, the network is more vulnerable to 51% attacks. Additionally, these validators also have the opportunity to abuse their power.
- Complex system setup: Requires significant coordination between all stakeholders to properly set up a Proof of Stake system. This can sometimes be difficult to achieve and may lead to delays in the system.
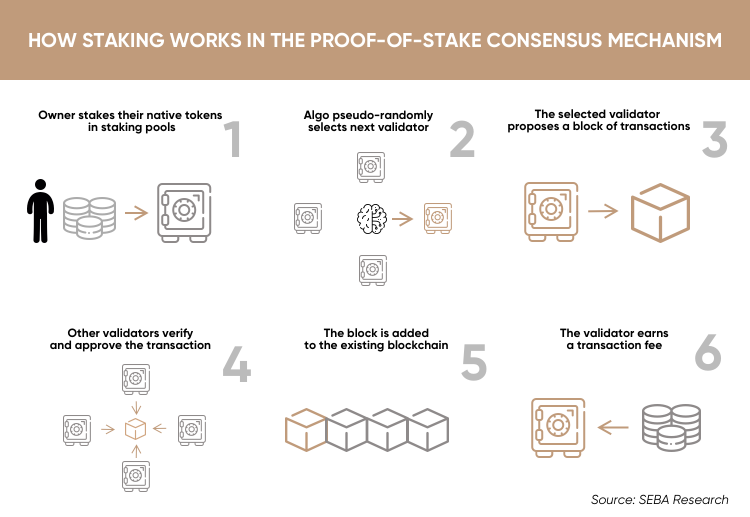
How Proof of Stake Works
With PoS, instead of mining new tokens, users can validate transactions in exchange for rewards.
The amount of reward is proportional to the number of tokens a user holds. This means that those holding larger amounts of tokens have a greater incentive to validate transactions, as they can earn more rewards.
These rewards can come from project token inflation (predefined in the token allocation or unlimited).
There are many ways to implement PoS, but the most common method is “Delegated Proof of Stake” (DPoS).
With DPoS, users vote for validators, who are then responsible for verifying transactions and committing them to the blockchain. Validators are rewarded with transaction fees and must also hold a certain amount of tokens to qualify for their position.
This system is designed to prevent centralization, as validators are chosen by the community rather than being appointed by a single entity. It also means that users can earn rewards even if they don’t hold a large number of tokens, as they can simply delegate their vote to a validator.
Currently, staking is not just limited to blockchain; it is also used in traditional projects to reduce circulating supply and selling pressure. In return, users who agree to lock up their tokens also receive rewards in the form of project tokens.
This method is currently widely used, but it’s a double-edged sword:
- Positive outcome: If, during the lock-up period, the project performs well and demonstrates why users should hold the token and not sell, there will be no selling pressure after the lock-up cycle ends.
- Negative outcome: Conversely, if nothing changes during this period, there’s a high probability that users will dump both the reward tokens and their original holdings, causing more severe damage to the project.
Read more: What is Staking? A Beginner’s Guide to Staking
Comparing Proof of Stake with Proof of Work
Proof of Stake and Proof of Work differ in several key aspects, including the associated costs and the level of control they give to transaction validators.
Read more: Learn About Proof of Work
The differences between Proof of Stake and Proof of Work are summarized in the comparison table below:

Read more: 3 Reasons Why Proof of Stake is More Secure Than Proof of Work
Is Proof of Stake Safe?
Proof of Stake is just a mechanism; it’s the specific project that determines its safety.
If the project is legitimate, staking tokens can provide additional rewards and allow users to genuinely contribute to the project’s development without needing to know how to code.
Unfortunately, if you choose a low-quality project or have poor security practices, there’s a high chance that the staked coins will be lost or significantly depreciate in value.
How to Mine PoS Coins
To mine PoS coins, users need to follow these 5 steps:
Step 1: Purchase a certain amount of the coin you intend to mine. The easiest way is to buy them on reputable exchanges, such as Binance or Huobi.
Step 2: Download the wallet for that coin and synchronize it with your computer. During synchronization, ensure your computer maintains a continuous internet connection. This process can take varying amounts of time depending on the coin.
Step 3: After synchronization is complete, keep your computer running 24/7 to stake. It is recommended to purchase a VPS (Virtual Private Server) for staking, as it will help you save on hardware investment, electricity costs for running the server, and installation space.
Step 4: After keeping the coins in your wallet for a while, they will mature and begin competing for blocks. Once your coins have secured a block and participated in creating a new block, you will receive rewards directly into your wallet.
Step 5: When you no longer want to stake or mine PoS coins, simply transfer the coins from your wallet to an exchange and sell them.
As I mentioned earlier, PoS is a form of coin mining using a stake-based system. This means that the amount of coins users mine depends on the number of coins they hold and the staking percentage allowed by the coin’s development team.
Example: The staking reward rate for Coin Buzz is 1200% per year, EMB is 7200% per year, and B3 is 10000% per year.
However, mining is not as simple as putting coins in a wallet and leaving it running 24/7 to achieve such huge profits. To maximize returns, users need to have a very high weight to compete with other stakers. The goal is to secure blocks as quickly as possible to earn coins.
So what is Weight? How to Achieve High Weight When Mining PoS Coins?
Weight (or the weight of a PoS coin) includes the coin age and the number of coins that users need to stake. Coin age is the time it takes for a coin to mature after being deposited into the coin wallet (this usually takes a few hours to a few days, depending on the coin).
After the coin matures, the weight will increase. The higher the weight, the greater the chance of winning a block. However, in the early stages, it will take a long time to mine PoS coins because:
- In the first block mined, after reaching sufficient weight, all the user’s coins will only mine one single block. However, these coins will be divided into multiple blocks afterward.
- After about 1-2 weeks, income will start to stabilize as the network net weight has been established.
- During the staking process, absolutely DO NOT add or withdraw coins, as these actions will erase all efforts to build the network net weight, and you will have to wait for it to rebuild.
Read more: 4 Tips for Effective Crypto Mining
Read more: If you need a product to assist with tax issues and portfolio management in crypto, check out CoinLedger

