To protect themselves from brute force attacks, users need to understand common brute force methods and why it can easily be successfully implemented in the crypto market.

What is Brute Force?
Brute force is a cyber attack method in which an attacker tries many different combinations of characters, passwords, or passcodes to discover security information such as passwords, PINs, or encryption keys.
This method is based on the principle of “trial and error” and continues to repeat combinations until the correct solution is found. Although this is a simple technique, with weak or insufficiently complex passwords, brute force is very effective.

In the realm of cryptocurrency (crypto), brute force attacks are a major threat because most digital wallets, transactions, and asset storage rely on strong passwords and complex encryption keys. Brute force can target both personal wallets and blockchain services, severely impacting digital assets if successful.
Some recent statistics show the severity of brute force attacks in the crypto market:
- A report from Chainalysis (2023) shows that brute force and phishing attacks contributed to over $4 billion in losses in the cryptocurrency market in 2023.
- Coinbase records thousands of failed login attempts daily into its system, most of which are due to brute force.
- Glassnode reports that approximately 20% of Bitcoin wallets currently have weak passwords or are assessed as vulnerable to attack.
Why is Brute Force Common in the Crypto Market?
In crypto, security has two core elements:
Private Key: This is a long string of characters (usually 256-bit) used to control your crypto assets. Private keys usually have a length of 256-bit, creating 2^256 possible combinations, or about 10^77 possibilities. Trying all combinations in this space is not feasible, even with today’s most powerful supercomputers.
To illustrate, if all the supercomputers in the world currently participated in brute-forcing a 256-bit key, the time required to try all combinations would still be too large, far exceeding the lifespan of the universe.Encryption keys in crypto are designed with sufficient length and randomness to resist brute force, and this protects them from being decrypted by “trial and error.” Therefore, brute force attacks often target users’ login passwords on exchanges or wallet applications, as passwords are usually shorter and less complex than private keys.
Login Password: This is a factor that many people easily overlook. Many people set short or easy-to-guess passwords (such as names, dates of birth, etc.), making these passwords attractive targets for brute force.
In a 2022 Bitwarden survey, only 40% of crypto users set passwords longer than 12 characters, and less than 30% enabled 2FA (two-factor authentication), paving the way for brute force. Large exchanges like Binance have recorded thousands of brute force attacks each month, targeting accounts with weak passwords or no two-factor authentication (2FA).
In addition, brute force is also easy to perform because automated attack tools are well-developed. Nowadays, hackers can use special software, like Hydra or John the Ripper, to automatically try thousands of password combinations in minutes. If the password is not strong enough, hackers can easily break in.
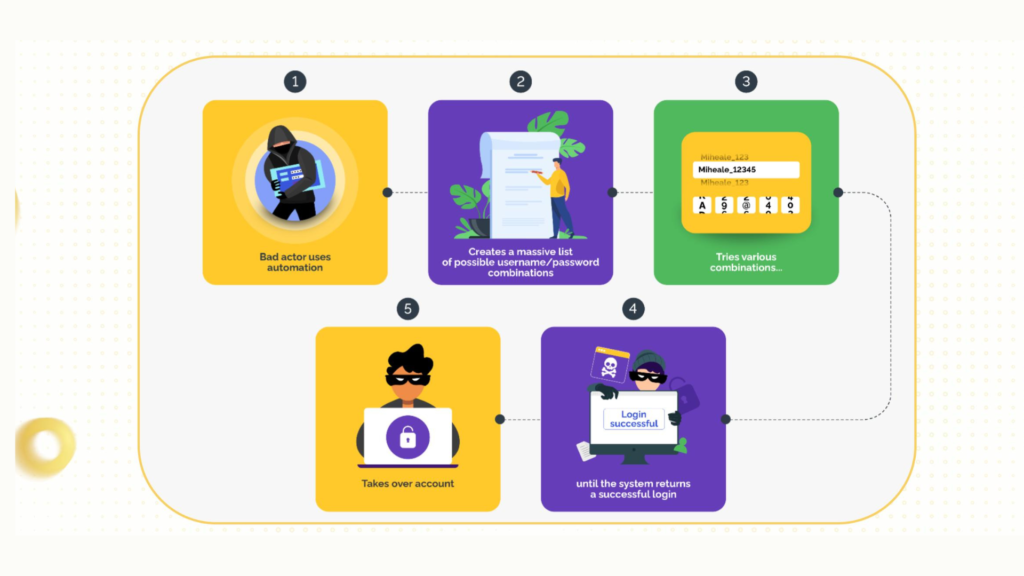
How to Protect Crypto Assets from Brute Force?
To reduce the risk from brute force, many large exchanges like Coinbase have implemented preventive measures such as limiting the number of incorrect entries, requiring OTP or using biometrics. However, users also need to protect themselves by:
- Using long and complex passwords.
- Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Storing private keys in a safe place.
In addition, cryptocurrencies do not have any intermediary agency to protect or recover assets in the event of an attack. This makes individuals and organizations vulnerable without strong security systems.
Learn: Safe ways to store Private Keys & Passphrases.
7 Common Brute Force Attack Methods
Simple Brute Force Attack
This is the simplest attack method, in which hackers try each character combination sequentially to find the password. This type of attack can be effective with short and simple passwords but is not suitable for long or highly secure passwords.
- Suitable for: Short passwords, few characters or no special characters.
- Weakness: For long and complex passwords, the attack time will be very long, almost impossible.
Dictionary Attack
This method uses a list of common words or frequently used passwords, called a “password dictionary,” and tries each word in the list to find the correct password. For those who use predictable or simple passwords, this attack can be effective.
- Suitable for: Users using common, easy-to-guess passwords.
- Weakness: Not effective with complex passwords that are not in the dictionary.
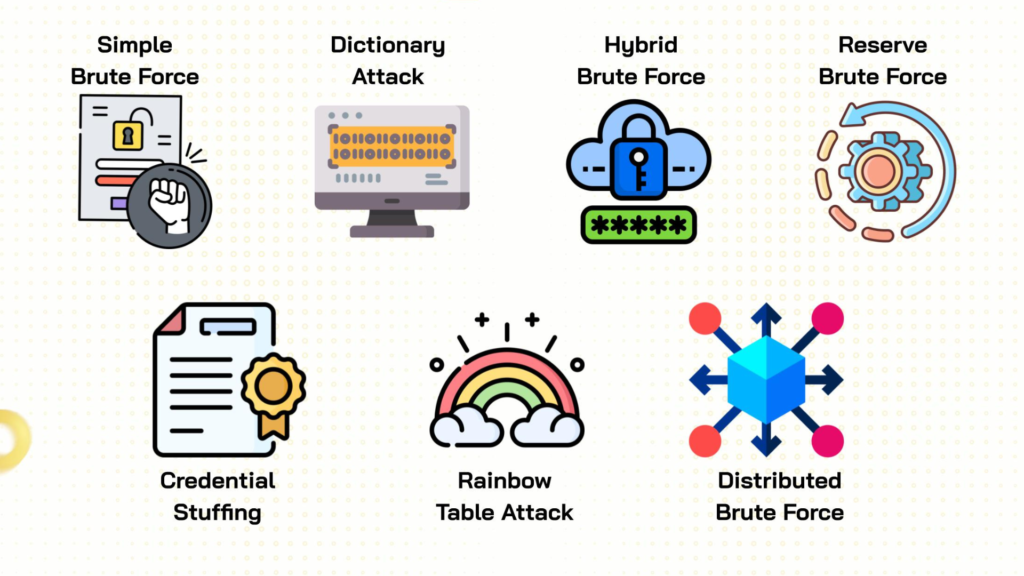
Reverse Brute Force Attack
Instead of guessing the password of one account, this method uses a common password to try to log in to many different accounts. This is how hackers check if any accounts are using predictable passwords.
- Suitable for: Systems with many accounts using common passwords.
- Weakness: Depends on whether any accounts are using this password.
Hybrid Brute Force Attack
A hybrid attack is a combination of a dictionary attack and brute force. Hackers use a word list (dictionary), then try adding characters, numbers, or special symbols to increase the chance of finding the password.
- Suitable for: Simple passwords with added numbers or symbols.
- Weakness: Takes longer than a dictionary attack, but is still less effective with very long or complex passwords.
Credential Stuffing
This is an attack method where hackers use login information leaked from previous security breaches and try to use it to access other accounts. This is especially effective if users reuse passwords across multiple accounts.
- Suitable for: Users using the same password across multiple services.
- Weakness: Not effective if users use unique passwords for each account.
Rainbow Table Attack
A rainbow table attack uses special lookup tables called rainbow tables, which contain passwords and their hash values. Hackers compare hash values in the table with the hash value of the password they are looking for to access the account.
- Suitable for: Passwords that are not encrypted or have weak hashing.
- Weakness: Must have rainbow tables beforehand, and if the system uses strong encryption algorithms, this method will be less effective.
Distributed Brute Force Attack
This is a way for hackers to use multiple devices or servers to simultaneously attack a system, minimizing the time it takes to find the password. By dividing the work among devices, distributed brute force increases the speed of password guessing.
- Suitable for: High security systems or complex passwords.
- Weakness: Requires large resources, difficult to implement with strong systems and measures to detect attackers.
What will Brute Force Attacks in Crypto Look Like in the Future?
Blockchain systems and crypto services are increasingly developing and applying new security technologies to deal with brute force. Some security trends in the future include:
Using Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) Wallets
Multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to complete a transaction. This enhances security because if one key is compromised, the hacker still cannot execute the transaction without the remaining keys. Multi-signature not only helps mitigate brute force risk but also helps users better control assets by dividing access rights. This is especially meaningful for organizations and users who own large amounts of assets, where security risks need to be spread across multiple layers.
Deploying Biometric Authentication Technology – Passkeys
Biometric authentication through Passkeys – security technologies such as fingerprint and facial recognition – is seen as an important step to mitigate brute force attacks in the crypto space.
By replacing traditional passwords with unique biometric identifiers, crypto can significantly reduce attacks targeting weak passwords. Biometric authentication also provides convenience and enhanced security, because biometric data is difficult to copy or guess through brute force tools.
Read more: What are Passkeys? The new authentication method in modern security
Sharing Security Through Zero-Knowledge Proof Technology
Zero-Knowledge Proof techniques allow users to prove access without revealing sensitive information. This is an ideal security method for crypto transactions because users can execute and confirm transactions without revealing any information about private keys or passwords. Zero-Knowledge Proof is highly regarded in blockchain security, helping to enhance privacy and mitigate the risk of brute force attacks when sensitive information is not disclosed.
Learn more: What is Zero-knowledge Proof? Advantages and limitations of ZKP technology.