How do crypto exchanges make money?
Ways that Crypto exchanges create huge profits for the development team.
For most people, October 3rd is just an ordinary day, but for Sam Bankman-Fried, it’s the day he appeared in court on charges of misusing customer funds, causing billions of dollars in damage.
Bankman-Fried, the founder of the now-defunct FTX exchange, is not the only one accused of defrauding investors through a crypto exchange.
Changpeng Zhao, the founder of Binance, also faces numerous allegations of money laundering, price manipulation, and investor fraud from the SEC.
In late 2022, the crypto exchange Celsius was also accused of conspiracy to defraud investors and had to pay $4.7 billion in compensation

All of these actions have caused concern among the crypto investment community, making the need for transparency regarding the business models and operations of crypto exchanges greater than ever. And one of the biggest questions investors have is: How are these exchanges making money?
This article will answer that question.

When it comes to highly profitable projects in the crypto market, exchanges often top the list. So where do they earn their main source of revenue?
The answer is listing fees.

“$15 million is the amount a project has to pay to be listed on a reputable centralized exchange (CEX), which is a pretty crazy number.”
Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, shared this with TechCrunch in an interview.
So why do projects agree to pay such large sums to exchanges?
The main reasons are marketing, reaching a huge user base, and boosting token prices, as reputable exchanges are where the highest liquidity is concentrated in the market.
In fact, many tokens have seen significant price increases after being listed on major crypto exchanges. For example, tokens from projects like District0x, Civic, and Near all increased from 100% to 645% after listing on Coinbase. Tokens listed on Binance also have an average increase of 73% after 30 days, according to CoinDesk
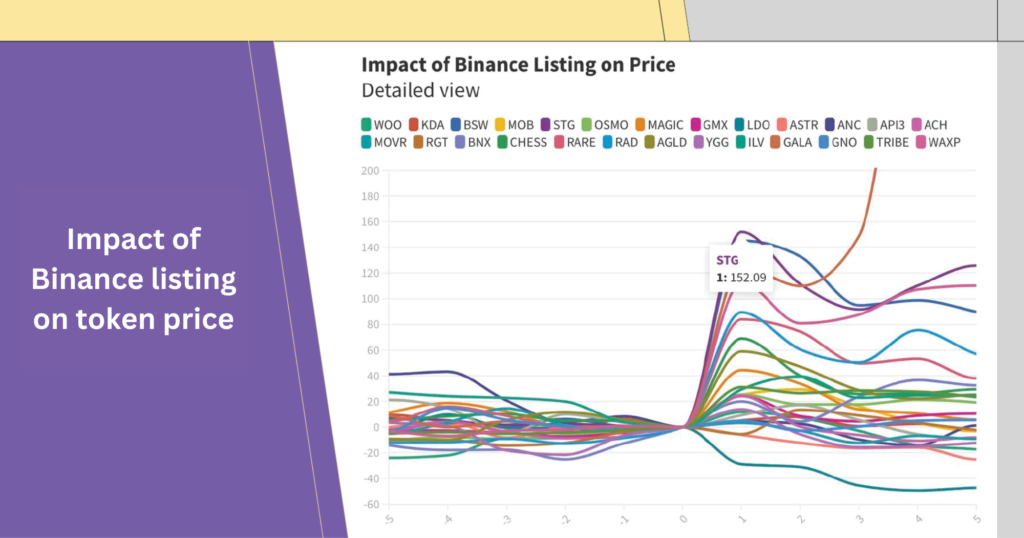
Of course, $15 million is not the standard figure. Listing fees vary depending on the size of the exchange and the reputation of the project. The larger the user base and trading volume on the exchange, the higher the listing fee.
According to the Blockchain Transparency Institute (BTI), the average listing fee ranges from $50,000 to $1 million. In months when countless projects launch, an exchange’s revenue can reach hundreds of millions of dollars per month.
This is understandable as exchanges recognize their value in the market and use listing fees to prevent low-quality projects from reaching investors.
Listing fees can sometimes be zero if the token belongs to a “hot” project with high trading demand. The exchange can earn a large amount of money from trading fees after listing such tokens.
Projects also benefit greatly if their tokens are invested in or listed by large and reputable exchanges. With a large existing user base, just one post on the exchange’s Twitter can have the same impact as a year’s worth of the project’s own marketing activities.
But do all exchanges that charge high listing fees have valid and reputable reasons for doing so?
A 2018 report by the BTI showed that the answer is not necessarily.
Over 90% of trades on exchanges like Bithumb and Bibox were found to be wash trades with the aim of deceiving projects and investors to justify high listing fees.
In 2019, the BKEX exchange carried out one of the laziest attempts to deceive users in history: Continuously copying Binance’s trading history and claiming it as their own. This made BKEX’s daily trading volume reach $1.1 billion and gave the exchange a “reasonable” justification to charge high listing fees.
However, exchanges cannot operate solely on listing fees, because in the absence of new projects, the exchange could cease to function. So what revenue sources do exchanges rely on to continue operating even when the market enters a downtrend?

It’s an obvious truth that the more users trade, the higher the transaction fees they have to pay.
Operating as an intermediary platform similar to Uber, Grab, or ShopeeFood, exchanges collect commission fees from both buyers and sellers.
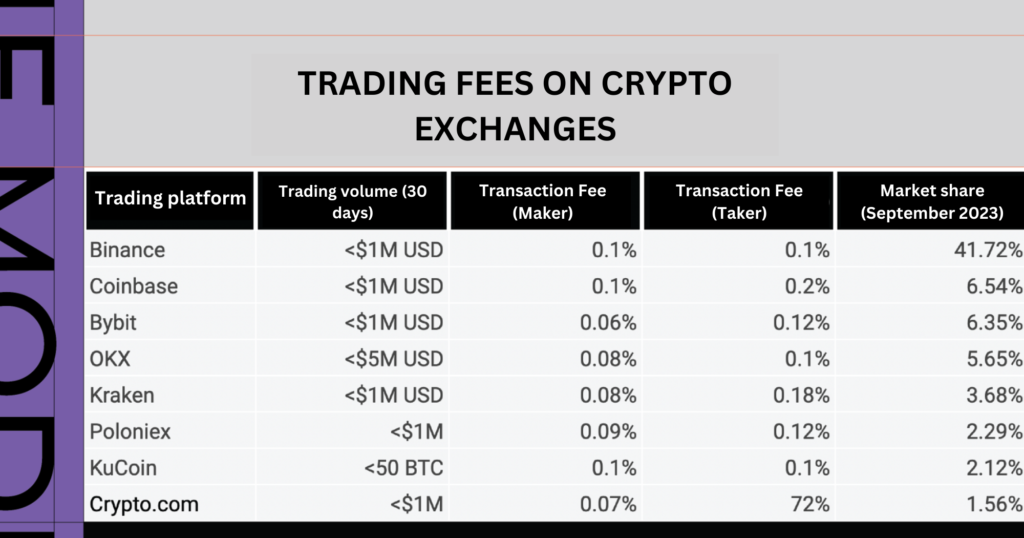
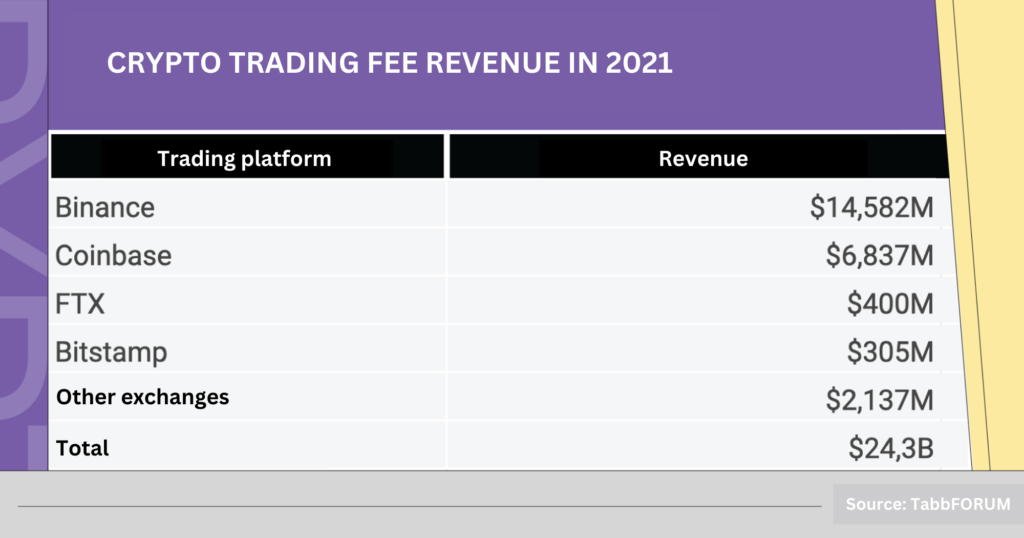
In Q1/2023, Binance’s spot trading volume was $1.534 trillion, generating $767 million in revenue. In 2018, even during a difficult period with fewer active users, Binance still generated $446 million in revenue.
This proves that exchanges can sustain operations even during the toughest times.
Besides spot trading, exchanges also collect fees from derivatives trading, OTC trading, margin trading, etc. Notably, derivatives trading is one of the key areas for crypto exchanges, as its total trading volume is even higher than spot trading.
Binance’s derivatives trading volume in Q1/2023 was $4.322 trillion, reaching $648 million in revenue. Meanwhile, OKX and Bybit only account for about half of Binance’s trading volume.
In addition, exchanges also offer copy trading services in both spot and derivatives markets, encouraging users to trade passively to increase trading volume. Bitget is the market leader in this area.
Commission fees help crypto exchanges earn huge profits, but is that enough to satisfy them?
Some argue that exchanges engage in other actions to increase their earnings, such as conducting large trades to influence token prices.
An SEC document revealed that Binance received 833,333 STX tokens, equivalent to $250,000, as a “long-term payment” to list Blockstack for one year.
Binance denied considering this a listing fee, as well as denying any actions to influence the price of the STX token. Instead, they stated that this was simply a marketing fee with the idea originating from Blockstack.
The practice of exchanges influencing token prices even occurs in the derivatives market. In this case, derivatives traders are both forced to liquidate their assets and pay additional liquidation fees to the exchange.
Furthermore, exchanges have another way to increase their value: issuing their own tokens

Why are Tokens Considered Financial Leverage for Exchanges?
The answer is that while traditional businesses need collateral to raise capital, crypto exchanges only need to issue exchange tokens.
Exchange tokens can be used as collateral to raise capital, helping exchanges continue to expand their operations. These activities can include acquiring other exchanges or websites, organizing events to attract new users, or investing in potential projects.
By allowing users to use tokens to pay for activities on the exchange or reducing fees for users who hold a large number of exchange tokens, exchanges drive high demand for their tokens. The token’s price and liquidity will correlate with the exchange’s user base.
Thanks to these advantages, most crypto exchanges like Binance, OKX, Bybit, Huobi, KuCoin, etc., have issued exchange tokens.
In the first half of 2023, despite the downtrend, some exchange tokens still performed well, even reaching new all-time highs (ATHs), especially MX (MEXC – up 225%), OKB (OKX – up 106%), BGB (Bitget – up 130%), and WOO (Woo Network – up 23.84%)…
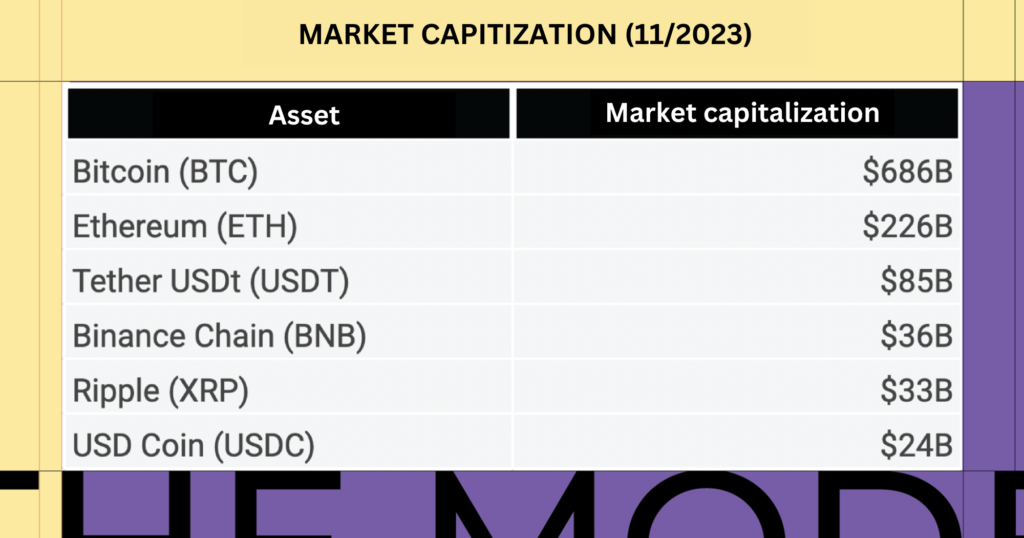
Binance is the exchange that benefits the most from issuing tokens. Although the price of the BNB token hasn’t increased much this year, its market capitalization currently ranks 4th, giving Binance strong momentum for development.
In 2022, Binance held numerous events around the world: Dubai, France, Spain, Portugal… to introduce its exchange and products. Previously, Binance also acquired the Sakura exchange, Trust Wallet, and Tokocrypto… and invested in potential crypto projects.
To increase its influence, Binance also organizes courses on blockchain and crypto, and even collaborates with universities to train and certify students.
Not just Binance, OKX also has many initiatives to expand its operations, such as sponsoring the Token2024 event in Singapore and developing a “hybrid custody model” that combines cold wallets (controlled by OKX) and warm wallets (stored by an intermediary). According to several sources, the investment in this product is up to $200 million.
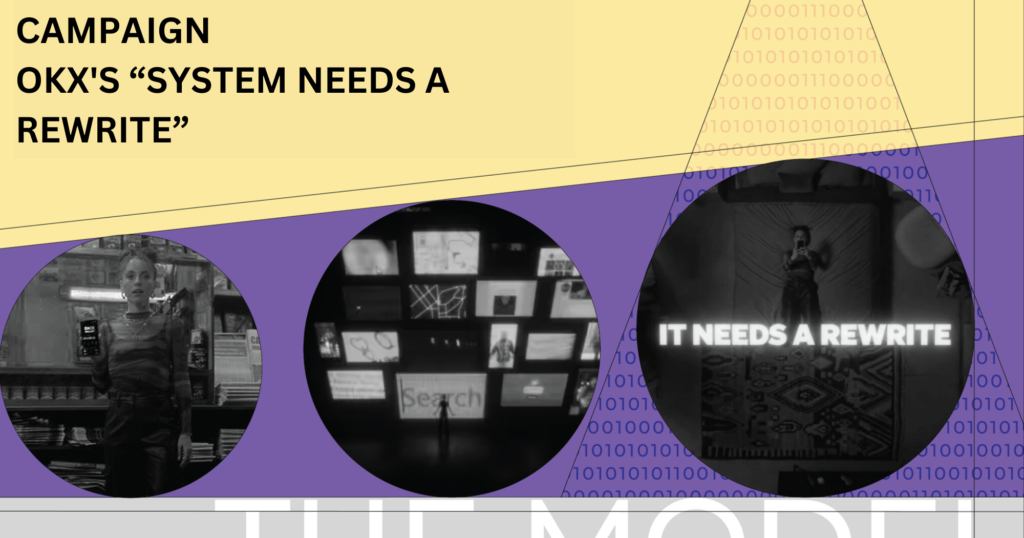
Recently, OKX also partnered with BBDO New York to carry out a global brand marketing campaign called “The System Needs a Rewrite.” With this campaign, OKX boldly challenges existing centralized systems and advocates for a new Web3 model managed by technology.
However, in addition to collecting fees and issuing tokens, crypto exchanges also have another way to make money.

[At the end of 2022, Binance Labs, the investment arm of Binance exchange, achieved a high return on investment of 2,100%, according to Binance News. The total assets managed by Binance Labs thus also accounted for $7.5 billion, according to the latest post on the fund’s blog.
The investment fund Coinbase Ventures, owned by Coinbase exchange, also reaped many achievements when it achieved a return of 15,700% from Terra (LUNA), 3,400% from Dodo (DODO), or 960% from Lido Finance (LDO).
Is this a general trend for investment funds?
To answer this question, let’s look at the investment results of the crypto investment fund Multicoin Capital, which lost 91.4% last year, according to CoinDesk.
Another crypto investment fund, Sequoia Capital, also apologized to investors for a $150 million loss in 2022, according to the WSJ.
Thus, it can be seen that the profits from investments by Binance Labs and Coinbase Ventures are not a general trend. So what is the difference between these two funds and other investment funds?
The answer is that Binance Labs and Coinbase Ventures are managed by exchanges, while the other funds are not.
Crypto exchanges often have an advantage over other investment funds in identifying potential projects. To be listed, projects must go through many rigorous due diligence steps by the exchange’s research team. Therefore, the exchange usually has full information on the projects listed on its platform.
As of now, there are more than 500 projects listed on Binance, 350 projects on OKX, and 240 projects on Coinbase.
With this information advantage, exchanges can easily make investment decisions or list tokens of potential projects for free. The growth of these projects also brings huge profits for the exchange’s investments and trading fees, as well as increases the exchange’s reputation.

It’s not uncommon for traders to struggle to connect with buyers or sellers due to a lack of information, relationships, or geographical distance. This situation leads to fragmented asset liquidity, making buying and selling difficult and hindering market growth.
Therefore, it’s clear that crypto exchanges play a vital role in the existence and development of cryptocurrencies. Thanks to exchanges, users can buy and sell crypto in seconds or maximize profits through services like staking and DCA.

Despite having a good business model, success doesn’t come easy for crypto exchanges.
To begin with, developers need significant capital to develop technology, infrastructure, marketing, and human resources. Additionally, exchanges are prone to facing legal issues, user data privacy concerns, and intellectual property rights challenges.
However, these difficulties also present opportunities for young entrepreneurs who want to enter the crypto market with a crypto exchange product.
Read more: How do Blockchain Projects Make Money?