What is Proof of Work? How does the PoW consensus mechanism work? Learn about the importance and disadvantages of Proof of Work here.

Alongside Proof of Stake, Proof of Work is an early consensus algorithm widely used in many blockchains. While many crypto investors may have heard of it, they might not fully understand what it is and how it works.
In this article, Coin98 Insights will explain Proof of Work in a simple way, without getting too technical, to make it easier for everyone to grasp.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
Proof of Work (PoW) was the first consensus mechanism created for blockchain and remains widely used in the cryptocurrency world. Satoshi Nakamoto successfully implemented Proof of Work for Bitcoin in 2009. Since then, PoW has become one of the most common consensus mechanisms in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Proof of Work brings together miners (also known as nodes) who compete to validate transactions and then include them in blocks on the blockchain to receive rewards, which vary depending on the network.
Example: Ethereum miners validate transactions on the Ethereum network, add them to blocks, and receive ETH as a reward.

How did Proof of Work come into being?
Although Satoshi Nakamoto was the first to implement Proof of Work (PoW) in a cryptocurrency, they weren’t the ones who originally conceived the idea. So, who created PoW, and when did the idea first emerge?
Here are the key milestones in the development of PoW:
- 1993: The earliest concept of Proof of Work was presented in the paper “Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail” by academics Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor. They proposed using computational work to deter denial-of-service (DoS, DDoS) attacks and email spam.
- 1997: Adam Back introduced a mechanism for preventing “double-spending” in his Hashcash whitepaper.
- 2004: Hal Finney applied the concept of PoW to cryptocurrency as a security solution through a mechanism called “Reusable Proof of Work.”
- 2009: Satoshi Nakamoto used Finney’s ideas to create the Proof of Work consensus mechanism for Bitcoin.
- 2009 – Present: Proof of Work has become a widely used consensus mechanism in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Read more: Impact of DDoS attacks in Crypto
Nature & how PoW works
The essence of Proof of Work is to validate someone’s proof of work to the entire blockchain network by expending real-world resources.
Example: Bitcoin’s PoW mechanism
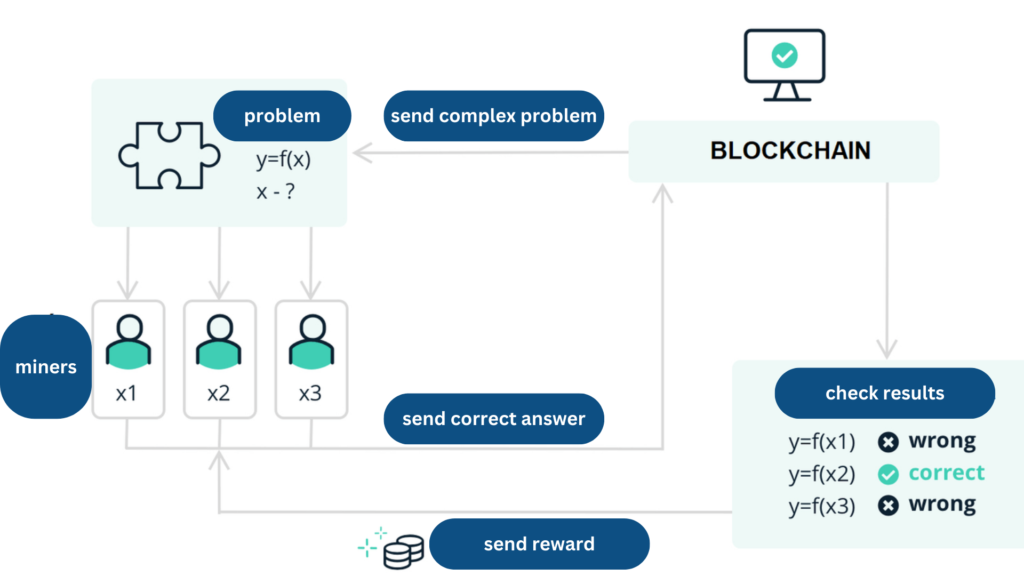
For the Bitcoin blockchain to function, new blocks need to be continuously generated to store transaction information.
This task is handled by “miners.” They have to solve complex mathematical problems and submit the correct answer to the entire network as quickly as possible.
To meet this requirement, miners need to use devices with high computing power, known as “mining rigs.” Operating these rigs requires electricity.
Therefore, the essence of Bitcoin’s PoW can be simplified as follows: Validating the proof of work (the correct answer to the problem) provided by miners to the entire Bitcoin blockchain network by expending real-world resources (mining rigs, electricity, and time).
Read more: 3 effective ways to mine Bitcoin for free
Importance of Proof of Work in Crypro
The purpose of PoW, from its initial conception to the present day, remains the same: to secure the network.
In blockchain, PoW’s primary function is to protect the network from Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. This is because attacking the network requires significant resources, such as computing power and time to solve complex mathematical problems, making such attacks extremely costly.
Furthermore, PoW minimizes the impact on a miner’s ability to participate. It doesn’t matter how many coins a miner holds in their wallet; as long as they have sufficient resources (computing power), they can participate in the mining process. If a miner lacks sufficient computing power, they can join a mining pool to leverage the combined computing power of the entire pool.
Disadvantages of Proof of Work
The two main weaknesses of the Proof of Work consensus mechanism are:
- Excessive resource consumption.
- Vulnerability to 51% attacks.
Energy Waste
This remains a hotly debated topic in the crypto community:
- One side argues that using excessive amounts of energy to maintain network security is wasteful.
- The other side contends that resource consumption is necessary to enhance network security.

Controversies Surrounding Proof of Work (PoW)
Energy Consumption Debate
The energy consumption of Proof of Work (PoW) has been a subject of ongoing debate.
Vulnerability to 51% Attacks
This is a critical issue, as 51% attacks are possible on blockchains that use PoW.
Read more: What is 51% Attack? How the 51% attack works
Why is this a concern?
As mentioned earlier, the PoW mechanism relies on computing power. So, what could happen if an individual or organization gains control of more than 51% of the network’s total computing power?
Essentially, that entity could take control of the network and validate fraudulent transactions, leading to double-spending, which could cause significant damage.
51% attacks are more likely to occur on smaller networks with fewer miners, as it’s easier to gain control of the network’s computing power. This is less likely to happen on large blockchain networks like Bitcoin because the cost of acquiring that much computing power is extremely high.
Below is a table showing the cost of carrying out a 51% attack, for your reference:

Conclusion
I’m sure that after reading this, those new to the cryptocurrency market will have grasped the definition of Proof of Work as well as the importance and weaknesses of this mechanism.


Pingback: Understanding Hash Functions in the Crypto Market - coinrin.com