The Bitcoin blockchain uses ECDSA signatures for transaction signing and authentication. However, ECDSA is gradually being replaced by Schnorr Signatures. Learn about Schnorr signatures in the following article.

What are Schnorr Signatures?
Schnorr signatures are a digital signature scheme based on elliptic curve cryptography, invented by Claus-Peter Schnorr, a German cryptographer. Schnorr signatures help verify the validity of transactions in cryptographic systems, based on mathematical principles related to prime modulo groups, allowing for the creation of concise signatures with high security.
Schnorr signatures are considered a more secure and efficient alternative to current digital signature algorithms like ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm).
Schnorr signatures have the following salient features:
- Compact size: Schnorr signatures are smaller than traditional ECDSA signatures, saving storage space.
- Fast processing speed: Signature verification is faster, improving network performance.
- Flexibility: Schnorr supports aggregate signatures, allowing multiple signatures to be combined into one, reducing transaction costs.
Benefits of Schnorr Signatures in general and compared to ECDSA
Enhanced Security
Schnorr signatures provide a higher level of security compared to ECDSA. It resists malleability attacks, a form of attack where the signature can be altered but remains valid, disrupting transactions. With Schnorr signatures, miners and transaction validators cannot manipulate signatures without being detected.
- Better anti-forgery: Schnorr uses strong mathematical principles, helping to prevent signature forgery attacks that ECDSA is more susceptible to.
- Resistance to hash-related attacks (Hash Collision): The way Schnorr creates signatures is less dependent on the security of the hash function than ECDSA, thereby reducing the risk of attacks due to hash collisions.
- Security in multi-signing scenarios: Schnorr minimizes the risk from reusing random values during the signing process, which is a serious vulnerability of ECDSA.
In addition, Schnorr signatures also help prevent replay attacks, a technique where attackers replay valid transactions for fraudulent purposes
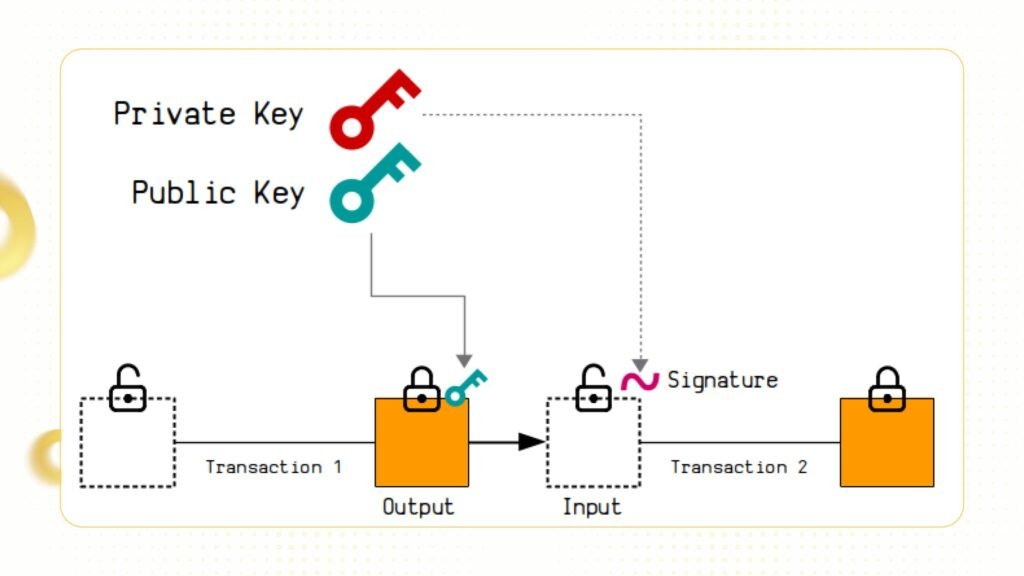
Optimizing Storage Space and Reducing Transaction Fees
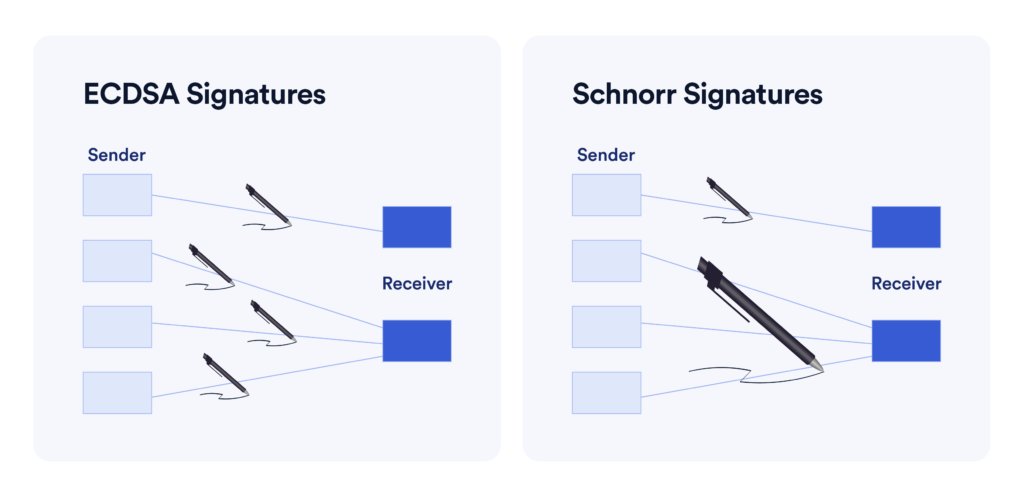
Thanks to the linearity of Schnorr signatures, multiple signatures can be combined into a single signature. This means that transactions with multiple participants (multisig) can be executed with one signature, instead of needing to create multiple individual signatures. This not only helps reduce transaction size but also reduces transaction fees on the network.
Example: A multisig transaction with 5 participants would require 5 individual signatures if using ECDSA, whereas with Schnorr signatures, all signatures can be combined into a single signature.
It can be seen that Schnorr signatures create smaller signatures than ECDSA, saving storage space on the blockchain.
Higher Performance in Complex Transactions
Schnorr signatures help speed up transaction processing and validation on the blockchain. Complex transactions, especially multi-signature (multisig) transactions or smart contracts, become faster and more efficient when using Schnorr signatures instead of traditional signature algorithms.
This not only helps reduce the burden on the network but also improves the user experience with lower costs and shorter transaction confirmation times. This is especially important for blockchains with large transaction volumes like Bitcoin.
Increased Privacy for Transactions Through Aggregate Signatures
Another advantage of Schnorr signatures is the ability to enhance privacy in transactions. By combining signatures into a single signature, multisig transactions become more difficult to identify. This helps protect the privacy of transaction participants, especially in the context of anonymous transactions being a major concern in the crypto market
Schnorr Signatures in Bitcoin and Taproot
Schnorr signatures were officially introduced to the Bitcoin network through the Taproot upgrade, activated on November 14, 2021, at block number 709,632. This is one of the most significant improvements to Bitcoin since the SegWit (Segregated Witness) upgrade in 2017. The Taproot upgrade was passed thanks to the consensus of the Bitcoin mining community, bringing major changes to the way transactions are processed on the blockchain.
Why are Taproot and Schnorr Signatures Important?
- The Taproot update helps Bitcoin:
- Become more efficient: Transactions become lighter and less expensive.
- Have better security: It is more difficult to analyze transactions or identify participants.
Open up new possibilities: Support advanced features such as smart contracts and multi-signature transactions. One of the key factors that makes Taproot different is the integration of Schnorr signatures. Schnorr significantly improves performance and security compared to the previous digital signature method (ECDSA) that Bitcoin used.
Learn: The implications of Bitcoin Taproot for the future of BTC.
How do Schnorr Signatures benefit Bitcoin?
By adopting Schnorr signatures, multi-signature transactions and smart contracts on Bitcoin can be executed more efficiently. This makes Bitcoin more versatile, suitable for more complex applications such as smart contracts and multi-party transactions.
This is an important step for Bitcoin to compete with other blockchains like Ethereum in deploying decentralized applications (dApps) or complex transactions.
How have Schnorr Signatures changed Bitcoin?
- More efficient: Faster transactions, cheaper fees, and saving storage space.
- Better security: Harder to distinguish between regular and complex transactions, increasing anonymity.
- More versatile: Supports advanced features like smart contracts, making Bitcoin more suitable for modern applications.
While Schnorr Signatures are seen as a major step forward in security and performance, limitations such as implementation difficulties, risks from quantum computing, and the potential for attacks remain challenges to be addressed. For Schnorr to be more widely adopted, developers and the blockchain community need to invest more in research, testing, and developing better support tools

